(!)Due to
Microsoft's end of support for Internet Explorer 11 on 15/06/2022, this site does not support the recommended
environment.
Instead, please kindly use other browsers like Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge or Mozilla
Firefox.
- Notice of End of Sales for Economy Series Pneumatic Equipment Category. More details.
How to Select Ball Screws: Page 1
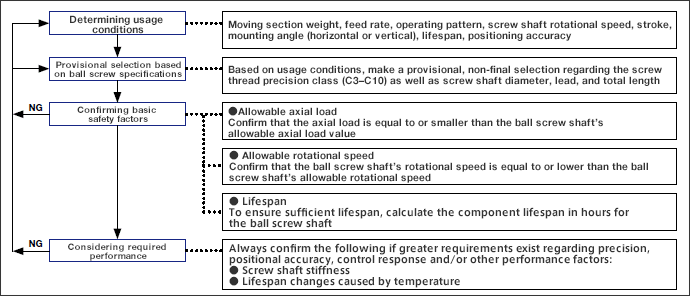
1. Ball Screw Selection Process
The following is an outline of the basic process for selecting ball screws, and relevant factors to consider.
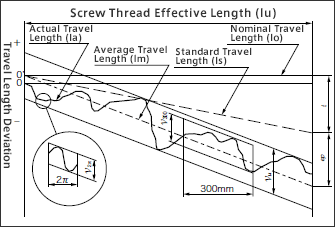
2. Ball Screw Lead Accuracy
Ball screw lead accuracy is a special characteristic stipulated under JIS standards (ep, Vu, V300, V2π).
Definitions and tolerance values for each are as described below.
In general, confirmation is made to determine whether the ball screw's average travel length deviation falls within tolerance values for positional accuracy when selecting a ball screw precision class.
| Term | Symbol | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Average travel length deviation | ep | Value obtained by subtracting standard travel length from average travel length. |
| Deviation range | Vu V300 V2π |
The following three items are determined based on the maximum amount of deviation of the actual travel length line positioned between the two lines drawn parallel to and on either side of the average travel length line: Maximum deviation relative to the maximum length of the screw thread Maximum deviation over a chosen 300-mm section relative to screw thread maximum length Maximum deviation over a chosen section comprising one rotation (2π rad) relative to screw thread maximum length |
| Standard travel length | ls | Axial travel length corrected for displacement caused by temperature rises, loads and/or similar, relative to nominal travel length (lo). |
| Standard travel length target value | t | Standard travel length relative to screw thread effective length, with nominal travel length subtracted. Used to determine displacement correction in cases where temperature changes, external loads and/or other such factors are expected to cause thread length elongation/contraction. Said values are determined experimentally and/or through practical experience. |
| Actual travel length | la | Actual, measured travel length. |
| Average travel length | lm | A straight line representing the general, average direction of actual travel. This line is calculated based on the curved line of actual travel length, using the least squares method or simple approximation method. |
Table 1: Positioning-use (C series) tolerance for average travel length deviation (±ep) and deviation range (vu) Unit: μm
| Screw Thread Effective Length (mm) | Precision Class | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C3 | C5 | ||||
| Exceeds | Max. | Average travel length deviation | Deviation range | Average travel length deviation | Deviation range |
| 315 | 12 | 8 | 23 | 18 | |
| 315 | 400 | 13 | 10 | 25 | 20 |
| 400 | 500 | 15 | 10 | 27 | 20 |
| 500 | 630 | 16 | 12 | 30 | 23 |
| 630 | 800 | 18 | 13 | 35 | 25 |
| 800 | 1000 | 21 | 15 | 40 | 27 |
| 1000 | 1250 | 24 | 16 | 46 | 30 |
| 1250 | 1600 | 29 | 18 | 54 | 35 |
Table 2: Positioning-use (C series) deviation range (V300) wobble (V2π) standard values for a 300-mm section Unit: μm
| Precision Class | C3 | C5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item | v300 | v2π | v300 | v2π |
| Standard Value | 8 | 6 | 18 | 8 |
Table 3: Conveyor-use (Ct series) deviation range (V300) standard values for 300-mm section Unit: μm
| Precision Class | Ct7 | Ct10 |
|---|---|---|
| v300 | 52 | 210 |
Conveyor-use (Ct series) average travel length (ep) is calculated as ep = 2 × lu ÷ 300 × V300.
3. Ball Screw Axial Clearance
Axial clearance is not an essential element of positional accuracy when travel is only in one direction. However, it may be a causal factor in backlash that affects positional accuracy when travel occurs in the reverse direction as well, when axial loads are applied, etc.
Select ball screw axial clearance specifications based on positional accuracy requirements.
Rolled ball screw
| Type | Common type(s) | Screw shaft diameter | Lead | Axial clearance | Screw shaft length (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | MAX | |||||
| Compact nut, precision class C10 | BSSC | 8 | 2 | Max. 0.05 | 100 | 400 |
| 10 | 4 | 150 | 600 | |||
| 12 | 4 | 150 | 800 | |||
| 15 | 5 | Max. 1.10 | 150 | 1,200 | ||
| 10 | 200 | 1,200 | ||||
| 20 | 5 | 200 | 2,000 | |||
| 10 | Max. 0.15 | 250 | 2,000 | |||
| 25 | 5 | Max. 1.10 | 200 | 2,000 | ||
| Standard nut, precision class C10 C-VALUE Standard nut precision class C10 |
BSSZ BSSR C-BSSC |
8 | 2 | Max. 0.05 | 100 | 400 |
| 4*1 | 100 | 380 | ||||
| 10 | 2*2 | 150 | 585 | |||
| 4 | 150 | 600 | ||||
| 10*1 | 150 | 585 | ||||
| 12 | 4 | 150 | 800 | |||
| 5*3 | 150 | 800 | ||||
| 10 | Max. 1.10 | 150 | 800 | |||
| 14 | 5* | 150 | 800 | |||
| 15 | 5 | 150 | 1,200 | |||
| 10 | 200 | 1,200 | ||||
| 16*4 | 200 | 1,200 | ||||
| 20 | 200 | 1,200 | ||||
| 20 | 5 | 200 | 2,000 | |||
| 10 | Max. 0.15 | 250 | 2,000 | |||
| 20 | Max. 1.10 | 250 | 2,000 | |||
| 25 | 5 | 200 | 2,000 | |||
| 10 | Max. 0.20 | 300 | 2,000 | |||
| 25 | Max. 0.12 | 300 | 2,000 | |||
| 28 | 6*3 | Max. 1.10 | 250 | 2,000 | ||
| 32 | 5*4 | Max. 0.20 | 300 | 2,000 | ||
| 10 | 300 | 2,000 | ||||
| 32 | Max. 0.15 | 300 | 2,000 | |||
| Block nut precision class C10 |
BSBR | 15 | 5 | Max. 1.10 | 150 | 1,200 |
| 20 | 200 | 1,200 | ||||
| 25 | 200 | 1,500 | ||||
| 15 | 10 | 150 | 1,200 | |||
| 20 | Max. 0.15 | 200 | 1,200 | |||
| 25 | Max. 0.20 | 200 | 1,500 | |||
| Standard nut precision class C7 |
BSST | 8 | 2 | Max. 0.03 | 100 | 380 |
| 10 | 4 | 150 | 585 | |||
| 12 | 4 | 150 | 795 | |||
| 15 | 5 | 150 | 1,200 | |||
| 10 | 200 | 1,200 | ||||
| 20 | 200 | 1,200 | ||||
| 20 | 5 | 200 | 1,200 | |||
| 10 | Max. 0.05 | 250 | 2,000 | |||
| 20 | Max. 0.03 | 250 | 2,000 | |||
| 25 | 5 | 200 | 2,000 | |||
| 10 | Max. 0.07 | 300 | 2,000 | |||
| C-VALUE Standard nut precision class C7 |
C-BSST | 8 | 2 | Max. 0.05 | 100 | 400 |
| 10 | 2 | 150 | 585 | |||
| 4 | 150 | 600 | ||||
| 12 | 4 | 150 | 800 | |||
| 5 | 150 | 800 | ||||
| 10 | Max. 1.10 | 150 | 800 | |||
| 15 | 5 | 150 | 1,200 | |||
| 10 | 200 | 1,200 | ||||
| 16 | 200 | 1,200 | ||||
| 20 | 200 | 1,200 | ||||
| 20 | 5 | 200 | 2,000 | |||
| 10 | 250 | 2,000 | ||||
| 20 | 250 | 2,000 | ||||
| 25 | 5 | 250 | 2,000 | |||
| 10 | 200 | 2,000 | ||||
| 25 | 300 | 2,000 | ||||
| 32 | 5 | 300 | 2,000 | |||
| 10 | Max. 0.14 | 300 | 2,000 | |||
| 32 | 300 | 2,000 | ||||
Notes
- *1 BSSR only
- *2 C-BSSC only
- *3 Not available for BSSZ
- *4 Not available for C-BSSC
Precision ball screw
| Type | Common type(s) | Screw shaft diameter | Lead | Axial clearance | Screw shaft length (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | MAX | |||||
| Standard nut, precision class C5 | BSS | 8 | 2 | Max. 0.005 | 100 | 210 |
| 10 | 2 | 100 | 315 | |||
| 4 | 150 | 380 | ||||
| 10 | 150 | 450 | ||||
| 12 | 2 | 150 | 445 | |||
| 4 | 150 | 400 | ||||
| 5 | 150 | 450 | ||||
| 10 | 200 | 600 | ||||
| 15 | 5 | 150 | 1,095 | |||
| 10 | 200 | 1,095 | ||||
| 20 | 230 | 1,095 | ||||
| 20 | 5 | 200 | 1,000 | |||
| 10 | 250 | 1,500 | ||||
| 20 | 250 | 1,500 | ||||
| 25 | 5 | 300 | 995 | |||
| 10 | 300 | 1,500 | ||||
| 20 | 300 | 1,500 | ||||
| C-VALUE Standard nut, precision class C5 |
C-BSS | 8 | 2 | Max. 0.008 | 100 | 210 |
| 10 | 2 | 100 | 315 | |||
| 4 | 150 | 380 | ||||
| 12 | 2 | 150 | 445 | |||
| 5 | 150 | 450 | ||||
| 10 | 200 | 600 | ||||
| 15 | 5 | Max. 0.015 | 150 | 1,095 | ||
| 10 | 200 | 1,095 | ||||
| 20 | 230 | 1,095 | ||||
| 20 | 5 | 200 | 1,000 | |||
| 10 | 250 | 1,500 | ||||
| 20 | 250 | 1,500 | ||||
| 25 | 5 | 300 | 995 | |||
| 10 | 300 | 1,500 | ||||
| 25 | 300 | 1,500 | ||||
| Standard nut precision class C3 |
BSX | 6 | 1 | 0 (preloaded part) |
80 | 205 |
| 8 | 1 | 80 | 255 | |||
| 2 | 100 | 240 | ||||
| 10 | 2 | 100 | 310 | |||
| 12 | 2 | 150 | 390 | |||
| 5 | 150 | 440 | ||||
| 15 | 5 | 150 | 590 | |||
| Standard nut precision class C7 |
BSSE | 8 | 2 | Max. 0.030 | 100 | 210 |
| 10 | 2 | 100 | 315 | |||
| 4 | 150 | 380 | ||||
| 12 | 2 | 150 | 445 | |||
| 5 | 150 | 450 | ||||
| 10 | 200 | 600 | ||||
| 15 | 5 | 150 | 1,095 | |||
| 10 | 200 | 1,095 | ||||
| 20 | 230 | 1,095 | ||||
| 20 | 5 | 200 | 1,000 | |||
| 10 | 250 | 1,500 | ||||
| 20 | 250 | 1,500 | ||||
| 25 | 10 | 300 | 1,500 | |||
| 20 | 300 | 1,500 | ||||
Example of Selecting Lead Accuracy
Usage conditions:
- Screw thread diameter is φ15, lead is 20
- Stroke is 720 mm
- Positional accuracy is ±0.05 mm / 720 mm
Selection:
Determine ball screw lead accuracy based on usage conditions to determine the appropriate precision class.
(1) Screw thread length
Stroke + nut length + excess: 720 + 62 + 60 = 842 mm
Note: "Excess" refers to an extra amount equivalent to 1.5 to 2 times the lead length, and is used as a measure against overrun.
Calculation based on a lead of 20 (with excess at both ends): 20 × 1.5 × 2 = 60.
(2) Lead accuracy
Using Table 1, calculate the tolerance for average travel length deviation ±ep based on a screw thread length of 842 mm.
C3・・・±0.021mm/800~1000mm
C5・・・±0.040mm/800~1000mm
(3) Lead accuracy selection
A C5 class (±0.040 / 800–1000 mm) screw is suitable for meeting positional accuracy usage conditions of ±0.05 mm / 720 mm.
Example of Selecting Axial Clearance
Usage conditions:
- Screw thread diameter is φ15, lead is 5
- Permissible backlash is ±0.01 mm
Selection:
According to Table 5, when using a screw with a thread diameter of φ15, a C5 class with max. 0.005 axial clearance fulfills the requirement of ±0.01-mm permissible backlash.