(!)Due to Microsoft's end of support for Internet Explorer 11 on 15/06/2022, this site does not support the recommended environment.
Instead, please kindly use other browsers like Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge or Mozilla Firefox.
50,000 Stock items for Same Day Ship Out.
All Categories
Categories
- Automation Components
A wide variety of standard and configurable components for factory automation engineers in industries such as automotive, semiconductor, packaging, medical and many more.
- Linear Motion
- Rotary Motion
- Connecting Parts
- Rotary Power Transmission
- Motors
- Conveyors & Material Handling
- Locating, Positioning, Jigs & Fixtures
- Inspection
- Sensors, Switches
- Pneumatics, Hydraulics
- Vacuum Components
- Hydraulic Equipment
- Discharging / Painting Devices
- Pipe, Tubes, Hoses & Fittings
- Modules, Units
- Heaters, Temperature Control
- Framing & Support
- Casters, Leveling Mounts, Posts
- Doors, Cabinet Hardware
- Springs, Shock Absorbers
- Adjusting, Fastening, Magnets
- Antivibration, Soundproofing Materials, Safety Products
- Fasteners
A good selection of accessories such as screws, bolts, washers and nuts that you may need for your daily engineering usage.
- Materials
Browse industrial materials ranging from heat insulating plates, sponges, to metal and plastic materials in different sizes to meet your various applications.
- Wiring Components
A wide variety of wiring parts for connecting and protecting control and PC parts including Connectors, Cables, Electric Wires, Crimping Terminals and more.
- LAN Cables / Industrial Network Cables
- Cables by Application
- Cables with Connectors
- RS232 / Personal Computers / AV Cables
- Wires/Cables
- Connectors (General Purpose)
- Crimp Terminals
- Zip Ties
- Cable Glands
- Cable Bushings/Clips/Stickers
- Screws/Spacers
- Cable Accessories
- Tubes
- Protection Tubes
- Ducts/Wiremolds
- General Purpose Tools
- Dedicated Tools
- Soldering Supplies
- Electrical & Controls
A wide variety of controls and PC parts for electrical engineers including Controls, Powers, PC parts and more.
- Cutting Tools
A wide variety of cutting tools for many uses and work materials including End Mills, Drills, Cutters, Reamers, Turning Tools and more.
- Carbide End Mills
- HSS End Mills
- Milling Cutter Inserts/Holders
- Customized Straight Blade End Mills
- Dedicated Cutters
- Turning Tools
- Drill Bits
- Screw-Hole-Related Tools
- Reamers
- Chamfering / Centering Tools
- Fixtures Related to Cutting Tools
- Step Drills
- Hole Saws
- Clean Key Cutters
- Core Drills (Tip Tools)
- Magnetic Drilling Machine Cutters
- Drill Bits for Electric Drilling Machines
- Woodworking Drill Cutters
- Drills for Concrete
- Processing Tools
A wide variety of tools and supplies used in processing including Machine Tools, Measurement Tools, Grinding and Polishing Supplies and more.
- Material Handling & Storage
A wide variety of goods used in shipment, material handling and warehouse including Tape supplies, Stretch film, Truck, Shelf, Crane and more.
- Tape Supplies
- Cushioning Materials
- Stretch Films
- Cardboard
- Plastic Bags
- PP Bands
- Magic Tapes / Tying Belts
- Rubber Bands
- Strings/Ropes
- Cable Ties
- Tags
- Labelers
- Unpacking Cutters
- Packing Support Equipment
- Cloth Sheets for Packing
- Conveyance/Dolly Carts
- Tool Wagons
- Tool Cabinets / Container Racks
- Lifters / Hand Pallets
- Container Pallets
- Storage Supplies
- Shelves/Racks
- Work Benches
- Suspended Clamps/Suspended Belts
- Jack Winches
- Chain Block Cranes
- Bottles/Containers
- Bicycle Storage Area
- Safety & General Supplies
A large variety of goods for every kind of factories and offices including Protection items, Cleaning supplies, sanitations, office supplies and more.
- Lab & Clean Room Supplies
A large variety of items used in R&D and Clean Room including research Equipment, Laboratory Essentials, Analysis Supplies, Clean Environment-Related Equipment and more.
- Press Die Components
Choose from thousands of standard stamping die components including Punch & Die, Gas Springs, Guide Components, Coil Springs and many more.
- Plastic Mold Components
Browse our wide variety of mold components including Ejector Pins, Sleeves, Leader Components, Sprue Bushings and many more.
- Ejector Pins
- Sleeves, Center Pins
- Core Pins
- Sprue bushings, Gates, and other components
- Date Mark Inserts, Recycle Mark Inserts, Pins with Gas Vent
- Undercut, Plates
- Leader Components, Components for Ejector Space
- Mold Opening Controllers
- Cooling or Heating Components
- Accessories, Others
- Components of Large Mold, Die Casting
- Injection Molding Components
Browse our injection molding components including Heating Items, Couplers, Hoses and more.
- Injection Molding Machine Products
- Accessories of Equipment
- Auxiliary Equipment
- Air Nippers
- Air Cylinders
- Air Chuck for Runner
- Chuck Board Components
- Frames
- Suction Components
- Parallel Air Chuck
- Special Air Chuck
- Chemical for Injection Molding
- Mold Maintenance
- Heating Items
- Heat Insulation Sheets
- Couplers, Plugs, One-touch Joints
- Tubes, Hoses, Peripheral Components
Search by Application
Brands
- Scheduled Maintenance Notice: This site will be unavailable due to scheduled maintenance from 9:00 9/2/2025 to 7:00 (SGT) 10/2/2025. We apologize for the inconvenience.
- Notice of End of Sales for Economy Series Pneumatic Equipment Category. More information.
LED Lighting Use Examples
Precautions for Mounting
(1) Installation Location
|
(2) Mounting Conditions
|
(3) Cable Mounting
If the cable sags, fix it with cable clips or similar.
Cable Terminal Diagram The cable terminal is semi-stripped. (excluding LED bulbs)
|
LZ10 Mounting Method
The body and the mounting bracket (accessory) are separate
(1) Fit the mounting bracket to both ends of the body
|
(2) With the mounting bracket fit in
|
(3) Mount to control panel interior or wall
|
LZ10 Dedicated Bracket
(1) Mount body in dedicated bracket
|
Control Panel Mounting Example
|
Aluminum Frame Mounting Example
|
Aluminum Frame Mounting Method
(1) Insert retrofit nut into aluminum frame
|
(2) Screw-fasten body and retrofit nut
|
LED Lighting Before Use
 Warning
Warning
- Do not connect to devices or power supplies with dimmer function. (Otherwise damage or smoke emission may result)
- Always turn power OFF before mounting, removing, or cleaning the instrument. (Otherwise, electric shock may result)
- Do not drape paper or cloth, etc., over the instrument. (Otherwise, fire may result)
- Never disassemble or modify the instrument. (Otherwise, fire or electric shock may result)
For the light bulb type
- Never use for emergency lighting instruments, guidance lighting instruments, or mercury lighting instruments, etc. (Otherwise damage or smoke emission may result)
 Caution
Caution
- Do not touch while lit or immediately after turning off, as it is hot. (Otherwise, burns may result)
- Do not look directly at the light emitting area while lit. (Otherwise, eye injury may result)
- Do not hit it with objects or scratch it. (Otherwise, damage may result)
- Use in a location with suitable environment. (Otherwise, damage may result)
- Make sure the instrument mounting is secure. (Otherwise, a fall may result)
- When dirty, wipe with a dry cloth. Do not use volatile organic solvents such as thinner, alcohol, or benzine.
(Otherwise, damage or discoloration may result) - Do not use in an environment exposed to volatile organic solvents or corrosive gases, etc. (Otherwise, damage may result)
- If the power line is affected by inductive noise etc., isolate the power line. (Otherwise, damage may result)
For the light bulb type
- Use a lamp at or below the instrument's specified wattage. (shortens lifetime)
- Make sure it is mounted securely in the socket. (Otherwise, a fall may result)
- Do not use where exposed to dripping water or high humidity. (Otherwise, damage may result)
Usage Precautions
- Since the LED elements vary in emission color and brightness, these properties may slightly differ even in the same model.
- Instrument illuminance, total luminous flux, and illuminance distribution are actual measured values and are not guaranteed.
Use as guidelines (reference values). - Use the color temperature value as a guideline (reference value).
- When mounting the instrument, fix it to a metal surface (aluminum frame or steel wall) with efficient heat dissipation.
- When wiring, always turn the power OFF first and make sure all wiring is correct.
- The power source has polarity (+ and -), so connect it correctly. The white cable is for the + side and the black one for the - side.
- Use voltage and current within the ranges indicated in the specifications.
- Use in an environment within the temperature and humidity ranges indicated in the specifications.
For the light bulb type
- Do not use a DC power supply.
- Do not use with a sealed or nearly sealed instrument, as it will lead to temperature increase and shortened lifetime.
- Do not use in a place where the lamp ambient temperature will exceed 40°C.
LED Lighting Terminology
LEDLED (Light Emitting Diode) means a semiconductor element which emits light when a current is run through it. |
IlluminanceThis refers to the brightness of the surface illuminated by the light source. |
|
Total FluxThis refers to the amount of light emitted from the light source in all directions. |
Color TemperatureThis is a measure for expressing the color of the light emitting by the light source as quantitative values. |
|
Light Distribution AngleThis refers to the angle at which the light is emitted from the light source. |
Illuminance DistributionThis refers to the brightness spread over the surface illuminated by the light source. |
|
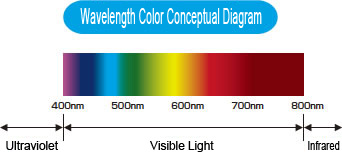
Emission SpectrumThis refers to the wavelength components and light strength emitted from the light source. |
LifetimeUnlike incandescent bulbs, LEDs do not fail to light due to broken filaments; however, the quantity of light produced gradually decreases due to deterioration of the materials used, etc. |
|
|
|

| The emission spectrum diagram shows the wavelength components and light strength emitted from the light source. Peak wavelength differs according to LED color. LED lighting does not contain ultraviolet harmful to substances and humans (400 nm or less). As well, yellow LEDs, with a 595 nm main component optimal for semiconductor manufacturing equipment etc., do not contain wavelength regions of 500 nm or less. Select the LED colors appropriate to your application. Note: LED elements have varying color and brightness, causing the emission spectrum to vary to some extent. Use as guidelines (reference values). |
 |




















