(!)Due to
Microsoft's end of support for Internet Explorer 11 on 15/06/2022, this site does not support the recommended
environment.
Instead, please kindly use other browsers like Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge or Mozilla
Firefox.
- Please be informed that there will be no shipment from Japan during the upcoming year-end and New Year holiday period. However, Singapore’s stock items are available during these periods. More details.
- Notice of End of Sales for Economy Series Pneumatic Equipment Category. More details.
Types and Uses of Metallic Materials 1
Steel types
| Type | Symbol | Examples of uses | Properties | JIS | Flat steel | Square steel | Hexagonal bar steel | Cylindrical rod | Steel plate | Steel beam |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Rolled steel for general structural use |
SS400 | General machine parts | Good workablity and weldability. | JIS G 3101 |
○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |
|
Cold finished steel bars (cold drawing) |
SS400-D | General machine parts | Good accuracy and surface roughness, and can be used as-is or with a small amount of cutting. | JIS G 3123 |
○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||
|
Carbon steel for machine structural use |
S45C | General machine parts |
Hardening is available. Tensile strength of 570 N/mm^2 (normalizing) |
JIS G 4051 |
○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |
| S50C |
Hardening is available. Tensile strength of 610 N/mm^2 (normalizing) |
|||||||||
| Alloy steel material for mechanical structures | SCM415 |
Machine parts requiring strength Screws, etc |
SCM435 Tensile strength of 930N / mm^2 or higher and hardness of 270 HB or higher after hardening and tempering |
JIS G 4053 |
○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |
| SCM420 | ||||||||||
| SCM435 | ||||||||||
| Carbon tool steel | SK95 (SK4) |
Shafts, pins, etc. |
Drill rod material (cylindrical rod) S95 material is cold drawn and finished by cutting. Grade 7 (-DG7) = h7 Grade 8 (-DG8) = h8 Grade 9 (-DG9) = h9 |
JIS G 4401 |
○ | ○ | ||||
| SK85 (SK5) |
○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||
| Alloy tool steel | SKS93 | Hardening parts | Far less deformation due to hardening than SK carbon steel materials. | JIS G 4404 |
○ | ○ | ○ | |||
| SKS3 | ||||||||||
|
Sulfur and sulfur composite free cutting steel Steel material |
SUM21 |
requiring strength (steel for free cutting) |
Free-cutting steel with sulfur added to carbon steel for improved machinability. | JIS G 4804 |
○ | ○ | ○ | |||
| SUM22L | Free-cutting steel to which lead is added in addition to sulfur. | |||||||||
| SUM24L | ||||||||||
|
High-carbon chrome Bearing steel |
SUJ2 | Rolling bearings, etc. | Bearing steel | JIS G 4805 |
○ | |||||
| Cold-rolled steel plate | SPCC | Covers, cases, etc. |
Produced by rolling at near room temperature. High dimensional precision with beautiful surface texture. Good workability for bending, drawing, and cutting. Good weldability. |
JIS G 3141 |
○ | |||||
| Hot-rolled mild steel plate | SPHC | Parts for general machine structures | Compatible thicknesses: 1.2 mm or more, 14 mm or less | JIS G 3131 |
○ |
Stainless steel types
| Classification | Symbol | Examples of uses | Properties | Magnetic properties | JIS | Flat steel | Square steel | Hexagonal bar steel | Cylindrical rod | Steel plate | Steel beam |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Austenite-base | SUS303 | Machine parts requiring rust prevention |
18-8-grade free-cutting stainless steel. Better cuttability than SUS304. |
No* | JIS G 4303 4304 4305 |
○ | ○ | ○ | |||
| SUS304 | The most versatile material as general corrosion resistant and heat-resistant steel. | No* | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||
| SUS316 | Better corrosion resistance than 304 to sea water and various media. | No* | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||
| Martensite-base | SUS410 | Machine parts requiring rust prevention (Corrosion resistance is inferior to austenite-base) |
Hardening is available. Good workablity. |
Yes | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||||
| SUS440C | Hardening is available. | Yes | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||||||
| Ferrite-base | SUS430 | Machine parts requiring rust prevention | General-use stainless steel with high corrosion resistance. | Yes | ○ | ○ | ○ |
**Machining on austenite-base may cause it to become magnetic.
<Reference: corrosion resistance of stainless steel>
- Test method
- Compliant with JIS H 8502
- cycle test method as a composite corrosion test
- Test conditions
- (1) Salt spray test (5% NaCl. 35°C) 2hr
- (2) Drying (60 °C) 4hr
- (3) Humidity (95% RH. 35°C) 2hr
- 1 cycle in 8hr
External appearance of specimen before the start of the test, after 48hr, and after 168hr
| SS400 | SUS440C | SUS304 | SUS316 | *G−STAR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before the start of the test |

|

|

|
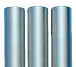
|

|
| 48hr |

|

|

|

|

|
| 168hr |

|

|

|

|

|
*G-STAR is martensitic stainless steel (pre-hardened steel) produced by Daido Steel Co., Ltd.
Aluminum alloy types
| Alloy number | Symbol | Examples of uses | Properties | JIS | Flat steel | Square steel | Cylindrical rod | Steel plate | Steel beam |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | A2011BE(S) A2011BD(S) A2011W(S) |
Volume shafts, optical parts, screws, etc. | It is as strong as 2017 and has very good milling properties but poor corrosion resistance. | JIS H 4000 4040 |
○ | ||||
| 2017 | A2017P A2017BE(S) A2017BD(S) A2017W(S) |
Machine parts, rivet materials, aviation materials, automotive parts, etc. | High strength is obtained by accelerated aging. Good milling properties, but poor corrosion resistance and weldability. | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||
| 5052 | A5052P A5052BE(S) A5052BD(S) A5052W(S) |
Ship materials, vehicle materials, construction materials, beverage cans, etc. | A typical medium-strength alloy with good corrosion resistance, moldability, and weldability. | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||
| 5056 | A5056BE(S) A5056BD(S) A5056W(S) |
Optical devices, communications device components, zippers, etc. | Excellent strength and ductility, good corrosion resistance, milling, and anodic oxidation treatment properties. | ○ | |||||
| 6005C (旧6N01) |
A6005CBE(S) | Structural materials, etc. | An alloy with strength between 6061 and 6063 and excellent extrudability and hardening. It has good corrosion resistance and can be welded. | ○ | ○ | ||||
| 6061 | A6061P A6061BE(S) A6061BD(S) A6061W(S) |
Rivet materials, bolt materials, automotive parts, etc. | Heat-treatable corrosion-resistant alloy. Aging gives considerable high proof stress values, but poor weldability. | ○ | ○ | ||||
| 6063 | A6063BE(S) A6063BD(S) |
Construction materials, civil engineering materials, furniture, home appliances, vehicle materials, etc. | A typical extrusion alloy. Lower in strength than 6061, but has excellent extrudability and good corrosion resistance, and surface treatment properties. | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||
| 7075 | A7075P A7075PC A7075BE(S) A7075BD(S) |
Aviation parts, rivet materials, etc. | One of the strongest aluminum alloys. | ○ | ○ |
The special class is indicated by (s).
Designations for types of aluminum alloys
| P | Plate |
|---|---|
| PC | Clad Plate |
| BE | Extruded Bar (normal class) |
| BD | Drawn Bar (normal class) |
| W | Drawn Wire (normal class) |
| TE | Extruded Tube (normal class) |
| TD | Drawn Tube (normal class) |
|---|---|
| TW | Welded Tube (normal class) |
| TWA | Arc-Welded Tube |
| S | Extruded Shape (normal class) |
| FD | Die Forging |
| FH | Hand Forging |
Temper designations of aluminum alloys
| Symbol | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| F | As-manufactured condition. The material is in an extruded form without thermal refining. | ||
| H112 | In expanded material, mechanical properties are guaranteed in the as-manufactured condition without aggressive work hardening. | ||
| H | H1n | H1 indicates only work hardening. | n is assigned a number from 1 to 9, indicating the degree of work hardening. If the number following H1 is 1, it means "1/8 hard"; H11 means an "expanded aluminum alloy that has been work-hardened only to become 1/8 hard"; 2 is "1/4 hard"; 3 is "3/8 hard"; 4 is "1/2 hard"; 5 is "5/8 hard"; 6 is "3/4 hard"; 7 is "7/8 hard"; 8 is "hard", and 9 is "extra hard." |
| H2n | H2 indicates work hardening followed by softening heat treatment. | ||
| H3n | H3 indicates work hardening followed by stabilization treatment. | ||
| O | The softest state of the product after annealing. | ||
| T | T1 | Naturally aged after cooling by high-temperature processing. Compatible with alloys such as 6063, where hardening is easily obtained by cooling after high-temperature processing (extrusion). | |
| T3 | Indicates solution annealing followed by cold working and natural aging. A cold working process is included to give higher strength and yield greater flatness and dimensional accuracy than T4 material. | ||
| T351 | After solution annealing, the alloy is cold worked to increase its strength, and residual stress is removed by tensile working to give a permanent strain of between 1.5% and 3%, followed by natural aging. | ||
| T4 | Indicates the state in which natural aging has been completed after solution treatment. In particular, T4 processed under the specified conditions at the consumer is referred to as T42. | ||
| T5 | Indicates artificially aged after cooling by high-temperature processing. Compatible with alloys and castings such as 6063, where hardening is easily obtained by cooling after high-temperature processing (extrusion). | ||
| T6 | Indicates artificially aged after solution treatment. Superior strength can be achieved without cold working through the typical heat treatment of a heat-treatable alloy. In particular, T6 processed under the specified conditions at the consumer is referred to as T62. | ||
| T61 | Indicates solution annealing by hot water hardening followed by artificial age-hardening treatment. | ||
| T651 | After solution annealing, residual stress is removed by tensile processing that imposes a permanent strain of between 1.5% and 3%, followed by natural aging. | ||
| T7 | Indicates stabilized after solution treatment. Performed to prevent corrosion stress fractures and protect against deformations and other faults that occur due to hardening. | ||
| T8 | Indicates solution treatment followed by cold working and then artificial age hardening treatment. | ||
| T9 | Indicates solution annealing treatment followed by artificial age hardening treatment and then cold working. | ||
PDF list
Help