(!)Due to
Microsoft's end of support for Internet Explorer 11 on 15/06/2022, this site does not support the recommended
environment.
Instead, please kindly use other browsers like Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge or Mozilla
Firefox.
- Please be informed that there will be no shipment from Japan during the upcoming year-end and New Year holiday period. However, Singapore’s stock items are available during these periods. More details.
- Notice of End of Sales for Economy Series Pneumatic Equipment Category. More details.
Drafting lines revised in 2010 (excerpt from JIS B 0001:2010)
Types and uses of lines
| Name by use | Line type c) | Line use | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Outline | Thick solid line |

|
Used to describe the shape of a visible part of the object. |
| Dimension line | Thin solid line |

|
Used for dimensioning. |
| Projection line | Used to project from a figure to note dimensions. | ||
|
Lead line (including reference lines) |
Used to indicate descriptions, symbols, etc. | ||
| Rotating section line | Used to represent a perspective of a part in the figure, rotated by 90°. | ||
| Centerline | Used to represent a simplified centerline in a figure. | ||
| Water level line a) | Used to indicate the position of a water, liquid, or other surface. | ||
| Hidden outline | Thin or thick dashed line |

|
Used to describe the shape of an invisible part of the object. |
| *Perforation line | Dashed spaced line |

|
Used to indicate the seam of cloth, leather, or sheet material. |
| *Association line | Dotted line |

|
Used to indicate the internal linkage of control equipment, interlocking operation of switchgear, etc. |
| Centerline | Thin long-dashed short-dashed line |
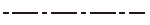
|
a) Used to represent the center of a figure. |
| b) Used to represent the central locus along which the center moves. | |||
| Reference line | Used to clearly indicate the basis of the location decision. | ||
| Pitch line | Used to represent the standard taking the pitch of a repeating figure. | ||
| Special requirement line | Thick long-dashed short-dashed line |

|
Used to indicate the extent to which special requirements should be applied, such as parts subjected to special processing. |
| Fictitious line b) | Thin long dashed double-dotted line |
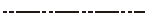
|
a) Used to represent adjacent areas for reference. |
| b) Used to indicate the position of tools, jigs, etc., for reference. | |||
| c) Used to represent a movable part at a specific position during movement or at the limit of movement. | |||
| d) Used to represent the shape before or after processing. | |||
| e) Used to indicate repetition. | |||
| f) Used to represent an area in front of an illustrated cross section. | |||
| Center of gravity line | Used to represent a line connecting the centers of gravity of a section. | ||
| *Optical axis line | Used to represent a line that shows the optical axis passing through a lens. | ||
| *Pipelines, wiring enclosure lines | Dashed dotted line |

|
Used to represent piping routes for water, oil, steam, water/sewage systems, etc. |
| Dashed double-dotted line |

|
||
| Dashed triple-dotted line |

|
||
| Long dashed dotted line |

|
Used to indicate certain functions by enclosing them in lines to distinguish between water, oil, steam, power supply sections, amplification sections, etc. | |
| Long dashed double-dotted line |

|
||
| Long dashed triplicate-dotted line |

|
||
| Double-dashed dotted line |

|
||
| Double-dashed double-dotted line |

|
Used to represent piping routes for water, oil, steam, etc. | |
| Double-dashed triple-dotted line |

|
||
| Break line | Thin solid or zig-zag lines with an irregular waveform |
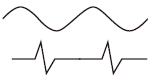
|
Used to represent a boundary that has been partially breached or partially removed from an object. |
| Section line | Thin long-dashed short-dashed line with ends and directional changes thickened. d) |
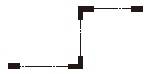
|
Used to represent the cross-sectional position on the corresponding figure when drawing a cross-sectional view. |
| Hatching | Thin solid lines, arranged in a regular pattern |

|
Used to distinguish a limited specific part of a figure from other parts. For example, a cross-sectional perspective is shown. |
| Special purpose lines | Thin solid line |

|
a) Used to represent extensions of outlines and hidden outlines. |
| b) Used to indicate a flat plane with two X-shaped lines. | |||
| c) Used to clarify or describe a location. | |||
| Extra thick solid line |

|
Used to illustrate a solid wire of thin-walled sections of rolled steel plate, glass, etc. | |
Notes
- a) Not specified in JIS Z 8316.
-
b) Fictitious lines are used to indicate shapes
that do not appear in the figure on a
projection but are necessary for convenience.
Also used to show additional figures as aids in understanding functional and processing aspects. (e.g., intermittent relationships by relay) - c) Other types of line should be according to JIS Z 8312 or JIS Z 8321.
- d) There is no need to use thick lines at the ends and for direction changes if there is no risk of mixing with other applications.
- *: Name of newly added use
PDF list
Help