(!)Due to
Microsoft's end of support for Internet Explorer 11 on 15/06/2022, this site does not support the recommended
environment.
Instead, please kindly use other browsers like Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge or Mozilla
Firefox.
- Notice of End of Sales for Economy Series Pneumatic Equipment Category. More details.
Excerpt from Surface roughness (JIS B 0601: 1994, JIS B 0031: 1994)
JIS B 0601 was amended in 2013.
- Types of surface roughness
- Typical method to obtain surface roughness
- Reference: The relationship with arithmetic average roughness (Ra) and conventional symbols
Types of surface roughness
As parameters that indicate the surface roughness of an industrial product, the definitions and
indications of the following parameters are specified: Arithmetic Average Roughness (Ra),
Maximum Height (Ry), 10-Point Height of Irregularities (Rz), Average Spacing of Irregularities
(Sm), Average Spacing of Local Peaks (S) and Load Length Ratio (tp). Surface roughness is the
arithmetic average value of a location randomly sampled from the surface of a subject.
[Average Centerline Roughness (Ra 75) is defined in the annexes of JIS B 0031 and JIS B 0601. 〕
Typical method to obtain surface roughness
Arithmetic Average Roughness (Ra)
This refers to a value obtained by the formula below and expressed in micrometers (µm) when sampling a section of reference length only from the roughness curve in the direction of the average line, taking the x-axis in the direction of the average line of the sampled section and the y-axis in the direction of vertical magnification to indicate the roughness curve with y = f(x).
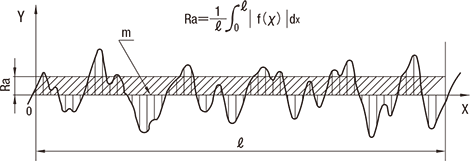
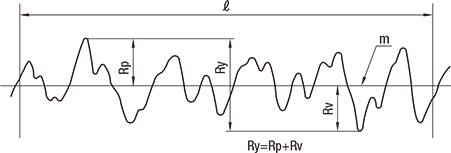
Maximum Height Ry *1
This refers to a value expressed in micrometers (µm) obtained by sampling a section of reference length only from the roughness curve in the direction of the average line and measuring the spacing between the peak line and bottom line of the sampled section in the direction of vertical magnification of the roughness curve.
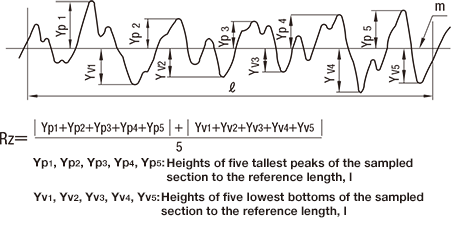
10-point height of irregularities Rz
This refers to a value expressed in micrometers (µm) obtained by sampling a section of reference length only from the roughness curve in the direction of the average line and calculating the sum of the average absolute value of the heights of 5 tallest peaks (Yp) and the average absolute value of the heights of 5 lowest bottoms (Yv) in the sampled section measured in the direction of vertical magnification from the average line.
Reference: The relationship with arithmetic average roughness (Ra) and conventional symbols*2
|
Arithmetic average roughness Ra |
Maximum height Ry |
10-point height of irregularities Rz |
Reference length of Ry or Rz, ℓ (mm) |
Conventional finish symbol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard sequence |
Cut-off value λc(mm) |
Illustration of surface texture | Standard sequence | |||
| 0.012 a 0.025 a 0.05 a 0.1 a 0.2 a |
0.08 |
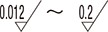
|
0.05 s 0.1 s 0.2 s 0.4 s 0.8 s |
0.05 z 0.1 z 0.2 z 0.4 z 0.8 z |
0.08 |

|
| 0.25 | ||||||
| 0.08 | ||||||
| 0.25 | 0.25 | |||||
| 0.8 | 0.25 | |||||
| 0.8 | 0.8 | |||||
| 0.4 a 0.8 a 1.6 a |
0.8 |

|
1.6 s 3.2 s 6.3 s |
1.6 z 3.2 z 6.3 z |
0.8 |

|
| 3.2 a 6.3 a |
2.5 |

|
12.5 s 25 s |
12.5 z 25 z |
2.5 |

|
| 12.5 a 25 a |
8 |

|
50 s 100 s |
50 z 100 z |

|
|
| 2.5 | ||||||
| 8 | ||||||
| 50 a 100 a |
8 |

|
200 s 400 s |
200 z 400 z |
8 |

|
| − | − | |||||
Notes
- *1 To obtain Ry, sample a portion only in the reference length from the part where there are no exceptionally high peaks or low bottoms which are deemed as scratches.
-
*2 The mutual relationship of the 3 types indicates a relationship for convenience only
and has no stringency.
Ra: The evaluation lengths of Ry and Rz are values 5 times the cut-off value and reference length respectively.