(!)Due to
Microsoft's end of support for Internet Explorer 11 on 15/06/2022, this site does not support the recommended
environment.
Instead, please kindly use other browsers like Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge or Mozilla
Firefox.
- Notice of End of Sales for Economy Series Pneumatic Equipment Category. More details.
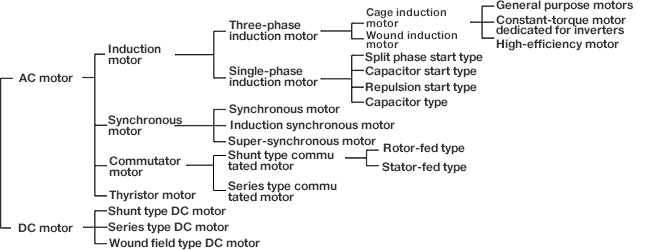
Types and Features of Motors
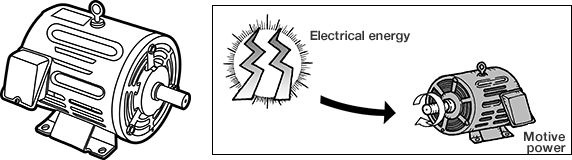
Motor
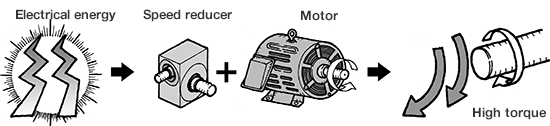
This is a machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy to obtain
motive power.
When electricity is passed through cables connected to the terminals, the motor converts the
electrical energy into mechanical energy and generates a force (torque) to turn the load on the
shaft, which transfers motive power to the corresponding machine.
Typical types of motors
Guide to motor selection
| DC motor (with brushes) | Stepper motor | AC motor (induction motor) | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Power supply: Direct current Easy to use due to excellent controllability and responsiveness. More expensive than AC motors and requires consumable parts (brushes). |
Rotation angle is controlled according to the number of input power supply pulses,
enabling high-precision control. Response speed is slower than other methods and requires electronic circuits to generate pulses. |
Power supply: Alternating current Relatively inexpensive and good for achieving larger sizes and higher outputs. |
|
| Long lifespan | ○ | ○ | |
| Low-speed rotation | ○ | ○ | |
| High efficiency | ○ | ||
| Low cost | ○ | ○ | |
| Positioning accuracy | ○ | ||
| Low noise | ○ | ○ | |
| High torque | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| Compact | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| Usage examples |
Fan motors for hair dryers Motors for drill screwdrivers |
Paper feed for printers Moving louvers of air conditioners |
Compressors Motors for drill presses |
Main points
- Check the voltage [single-phase (V)/three-phase (V)] of the power supply [direct current (DC)/alternating current (AC)].
- Check the rotational speed (rpm).
- Check the required torque/output (W).
- Check the mounting method (leg mounting, flange mounting, etc.).
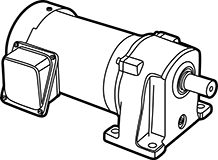
Gear motor
This is a motor integrated with a speed reducer.
Parallel shaft leg mounting type
Parallel shaft flange mounting type
Orthogonal shaft type
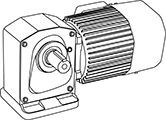
Features
- A reduction gear is attached to the motor, and this drive unit provides lower revolution and higher torque than the motor alone.
- There are two methods of mounting on the machine: leg-mounted and flange-mounted.
Motor with clutch brake
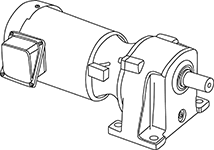
Features
- This gear motor rotates by a three-phase 200 V power supply and has a clutch brake. It is used when you want to use intermittent driving that repeatedly stops and rotates. There are two types of mounting: leg-mounted and flange-mounted.
Structural drawing
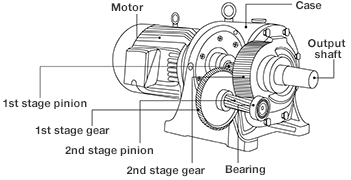
Useful info
Reduction ratio
· Low gear of a car = High reduction ratio
Reduction ratio 1/100

· High gear of a car = Low reduction ratio
Reduction ratio 1/10

Main points
- Check the power supply. (single-phase 100 V or three-phase 200 V)
- Check the motor capacity (W).
- Check the rotational speed (rpm).
- Check the reduction ratio.
- Check whether or not a gear motor can be connected to the machine.
- Determine the reduction ratio according to the required rotational speed torque.
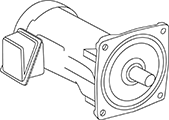
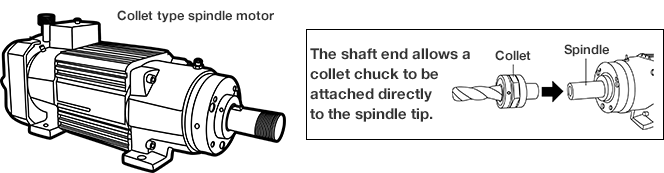
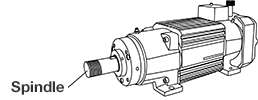
Spindle motor
This is a compact motor with the motor and spindle (rotary shaft) integrated into a single
structure.
Spindle motor
Features
- The shaft of the induction motor is used as the spindle, etc., to which tools can be attached, eliminating the need to separate the motor and spindle by pulleys, couplings, etc. This leads to more compact machines, improved mechanical accuracy, and cost reductions.
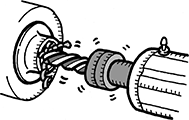
Various types are available.
The motor and spindle are integrated into a single structure, leading to more compact
machines, improved mechanical precision, and cost reductions.
· Separated
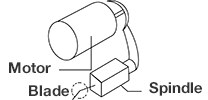
· Integrated
Circular saw motor
Simply inputting 200 V commercial power (50/60 Hz) to the motor causes it to rotate.
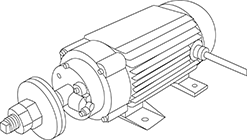
Features
- A fitting for attaching a circular saw to the spindle is included.
Types of attachments
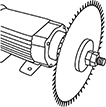
· Circular saw attachment
Can be used for cutting wood and metal by attaching a circular saw.
· Cutter attachment
Can be used for grooving wood and metal by attaching a cutter.
· Buffing tool attachment
Can be used for surface polishing, etc., by attaching a buffing tool.
Main points
- Check the rotational speed (rpm).
- Check the required torque/output (W).
- Select a blade that is appropriate for the material to be cut.
- Specify the direction that the motor rotates.
Reference: Coco Mite Vol. 2