(!)Due to
Microsoft's end of support for Internet Explorer 11 on 15/06/2022, this site does not support the recommended
environment.
Instead, please kindly use other browsers like Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge or Mozilla
Firefox.
- Notice of End of Sales for Economy Series Pneumatic Equipment Category. More details.
Screw Type / Appropriate Tightening Axial Force of Bolt / Appropriate Tightening Torque (Fundamentals of Screw)
Screw Type
Thread shape
Triangular screw thread
Common fastening parts
Square thread
It is used when strong force is applied to the screw thread
Mainly used in power transmission area (jacks, vices, etc.)

Trapezoidal lead screw
Used in precise motion transmission areas (lathe feed screws, etc.)
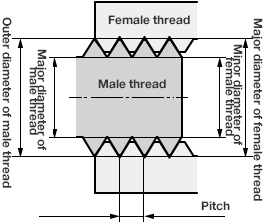
Male thread and female thread
| Standard | Symbol | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Metric coarse thread | M | M3 |
| Metric fine thread | M (with pitch) | M3 x 0.35 |
| Unified coarse thread | UNC | 3/4-10UNC |
| Unified fine thread | UNF | 1/2-20UNF |
| Parallel pipe thread | G, PF | G1/2 |
| Tapered pipe thread | R, PT | R3/4 |
* Metric threads are according to JIS B 0205 (1997) for coarse threads and JIS B 0207 (1982) for fine threads.
Male thread
Those with threads on the outside of a cylindrical body or conical body
Female thread
Those with threads on the inside
Screws are used in combination with male and female threads, so the dimensions of each must
match.
That is to say, fastening is not possible unless the nominal numbers are the same.
Material
Requirements for screw materials
- Low cost and easy to obtain
- With strength and toughness, and machining is possible
- Properties can be changed widely by appropriately selecting components and heat treatments
Typical materials
- Steel alloy SCM (chrome molybdenum steel): Standard
- Stainless steel SUS: It is used in locations where corrosion and outlet gas emissions are undesirable

Surface treatment
- Black oxide coating
- Bright chromate plating


Appropriate Tightening Axial Force of Bolts / Appropriate Tightening Torque
The torque method is widely used because of its simplicity
Tightening axial force and fatigue limit when fastening with bolts
- Calculation of the appropriate tightening axial force when tightening bolts shall be within the elastic range, that is up to 70% of the standard yield strength in the torque method.
- Fatigue strength of bolts due to repeated load shall not exceed the allowable value.
- The fastened object shall not be recessed on the bolt and nut bearing surfaces.
- The fastened object shall not be damaged by tightening.
Calculation of tightening axial force and tightening torque
- Tightening axial force
- Ff=0.7・σy・As
- Tightening torque
- TfA=0.35k(1+1/Q)σy・As・d
- k
- : Torque coefficient
- d
- : Bolt nominal diameter [cm]
- Q
- : Tightening coefficient
- σy
- : Yield strength (112 kgf/mm2 when strength class 12.9)
- As
- : Bolt effective cross-sectional area (mm2)
<Calculation examples>
When tightening mild steel to mild steel with M6 hex socket head cap screw (strength class 12.9) under oil lubrication
Axial force is
- Ff
- =0.7・σy・As
- =0.7・112・20.1
- =1576[kgf]
Appropriate torque is
- TfA
- =0.35k(1+1/Q)σy・As・d
- =0.35・0.175(1+1/1.4)112・20.1・0.6
- =142[kgf・cm]
| Bolt surface treatment lubrication |
Torque coefficient k |
Combination 
|
|---|---|---|
|
Steel bolt Black oxide coating Oil lubrication |
0.145 | SCM-FC FC-FC SUS-FC |
| 0.155 | S10C-FC SCM-S10C SCM-SCM FC-S10C FC-SCM | |
| 0.165 | SCM-SUS FC-SUS AL-FC SUS-S10C SUS-SCM SUS-SUS | |
| 0.175 | S10C-S10C S10C-SCM S10C-SUS AL-S10C AL-SCM | |
| 0.185 | SCM-AL FC-AL AL-SUS | |
| 0.195 | S10C-AL SUS-AL | |
| 0.215 | AL-AL | |
|
Steel bolt Black oxide coating No lubrication |
0.25 | S10C-FC SCM-FC FC-FC |
| 0.35 | S10C-SCM SCM-SCM FC-S10C FC-SCM AL-FC | |
| 0.45 | S10C-S10C SCM-S10C AL-S10C AL-SCM | |
| 0.55 | SCM-AL FC-AL AL-AL |
- S10C
- : Untempered mild steel
- SCM
- : Heat-treated steel (35JRC)
- FC
- : Cast iron (FC200)
- AL
- : Aluminum
- SUS
- : Stainless steel (SUS304)
|
Tightening coefficient Q |
Tightening method | Surface condition | Lubrication condition | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bolt | Nut | |||
| 1.25 | Torque wrench | Manganese phosphate | Not treated or phosphate | Oil lubrication or MoS2 paste |
| 1.4 | Torque wrench | Not treated or phosphate | ||
| Wrench with torque limit | ||||
| 1.6 | Impact wrench | |||
| 1.8 | Torque wrench | Not treated or phosphate | Not treated | No lubrication |
| Wrench with torque limit | ||||
