(!)Due to Microsoft's end of support for Internet Explorer 11 on 15/06/2022, this site does not support the recommended environment.
Instead, please kindly use other browsers like Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge or Mozilla Firefox.
50,000 Stock items for Same Day Ship Out.
All Categories
Categories
- Automation Components
A wide variety of standard and configurable components for factory automation engineers in industries such as automotive, semiconductor, packaging, medical and many more.
- Linear Motion
- Rotary Motion
- Connecting Parts
- Rotary Power Transmission
- Motors
- Conveyors & Material Handling
- Locating, Positioning, Jigs & Fixtures
- Inspection
- Sensors, Switches
- Pneumatics, Hydraulics
- Vacuum Components
- Hydraulic Equipment
- Discharging / Painting Devices
- Pipe, Tubes, Hoses & Fittings
- Modules, Units
- Heaters, Temperature Control
- Framing & Support
- Casters, Leveling Mounts, Posts
- Doors, Cabinet Hardware
- Springs, Shock Absorbers
- Adjusting, Fastening, Magnets
- Antivibration, Soundproofing Materials, Safety Products
- Fasteners
A good selection of accessories such as screws, bolts, washers and nuts that you may need for your daily engineering usage.
- Materials
Browse industrial materials ranging from heat insulating plates, sponges, to metal and plastic materials in different sizes to meet your various applications.
- Wiring Components
A wide variety of wiring parts for connecting and protecting control and PC parts including Connectors, Cables, Electric Wires, Crimping Terminals and more.
- LAN Cables / Industrial Network Cables
- Cables by Application
- Cables with Connectors
- RS232 / Personal Computers / AV Cables
- Wires/Cables
- Connectors (General Purpose)
- Crimp Terminals
- Zip Ties
- Cable Glands
- Cable Bushings/Clips/Stickers
- Screws/Spacers
- Cable Accessories
- Tubes
- Protection Tubes
- Ducts/Wiremolds
- General Purpose Tools
- Dedicated Tools
- Soldering Supplies
- Electrical & Controls
A wide variety of controls and PC parts for electrical engineers including Controls, Powers, PC parts and more.
- Cutting Tools
A wide variety of cutting tools for many uses and work materials including End Mills, Drills, Cutters, Reamers, Turning Tools and more.
- Carbide End Mills
- HSS End Mills
- Milling Cutter Inserts/Holders
- Customized Straight Blade End Mills
- Dedicated Cutters
- Turning Tools
- Drill Bits
- Screw-Hole-Related Tools
- Reamers
- Chamfering / Centering Tools
- Fixtures Related to Cutting Tools
- Step Drills
- Hole Saws
- Clean Key Cutters
- Core Drills (Tip Tools)
- Magnetic Drilling Machine Cutters
- Drill Bits for Electric Drilling Machines
- Woodworking Drill Cutters
- Drills for Concrete
- Processing Tools
A wide variety of tools and supplies used in processing including Machine Tools, Measurement Tools, Grinding and Polishing Supplies and more.
- Material Handling & Storage
A wide variety of goods used in shipment, material handling and warehouse including Tape supplies, Stretch film, Truck, Shelf, Crane and more.
- Tape Supplies
- Cushioning Materials
- Stretch Films
- Cardboard
- Plastic Bags
- PP Bands
- Magic Tapes / Tying Belts
- Rubber Bands
- Strings/Ropes
- Cable Ties
- Tags
- Labelers
- Unpacking Cutters
- Packing Support Equipment
- Cloth Sheets for Packing
- Conveyance/Dolly Carts
- Tool Wagons
- Tool Cabinets / Container Racks
- Lifters / Hand Pallets
- Container Pallets
- Storage Supplies
- Shelves/Racks
- Work Benches
- Suspended Clamps/Suspended Belts
- Jack Winches
- Chain Block Cranes
- Bottles/Containers
- Bicycle Storage Area
- Safety & General Supplies
A large variety of goods for every kind of factories and offices including Protection items, Cleaning supplies, sanitations, office supplies and more.
- Lab & Clean Room Supplies
A large variety of items used in R&D and Clean Room including research Equipment, Laboratory Essentials, Analysis Supplies, Clean Environment-Related Equipment and more.
- Press Die Components
Choose from thousands of standard stamping die components including Punch & Die, Gas Springs, Guide Components, Coil Springs and many more.
- Plastic Mold Components
Browse our wide variety of mold components including Ejector Pins, Sleeves, Leader Components, Sprue Bushings and many more.
- Ejector Pins
- Sleeves, Center Pins
- Core Pins
- Sprue bushings, Gates, and other components
- Date Mark Inserts, Recycle Mark Inserts, Pins with Gas Vent
- Undercut, Plates
- Leader Components, Components for Ejector Space
- Mold Opening Controllers
- Cooling or Heating Components
- Accessories, Others
- Components of Large Mold, Die Casting
- Injection Molding Components
Browse our injection molding components including Heating Items, Couplers, Hoses and more.
- Injection Molding Machine Products
- Accessories of Equipment
- Auxiliary Equipment
- Air Nippers
- Air Cylinders
- Air Chuck for Runner
- Chuck Board Components
- Frames
- Suction Components
- Parallel Air Chuck
- Special Air Chuck
- Chemical for Injection Molding
- Mold Maintenance
- Heating Items
- Heat Insulation Sheets
- Couplers, Plugs, One-touch Joints
- Tubes, Hoses, Peripheral Components
Search by Application
Brands
- Notice of End of Sales for Economy Series Pneumatic Equipment Category. More information.
What are Industrial Materials?: Metallic Material Basics (Industrial Material and Surface Treatment Basics)
This article is designed to help users select materials with greater confidence by providing a brief introduction to the characteristics and selection methods of basic materials and surface treatments.
- What are Industrial materials?: Metallic material basics
- Frequently Used Metallic Materials
- What is Heat Treatment? / What is Surface Treatment?
What are industrial materials?
There are four main categories of industrial materials. This special feature focuses on the metallic materials.
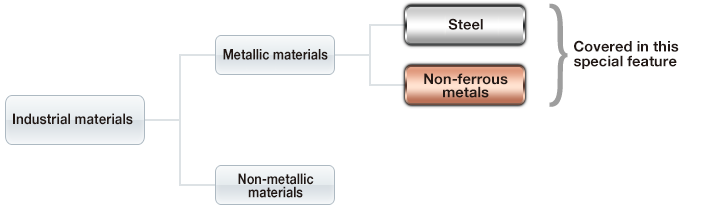
Metallic material basics
Review of terminology used in material standards and for describing mechanical/physical properties
Material standards
Standards have been created for industrial materials to make it easier to identify their properties and compare different materials.
The JIS standards (Japanese Industrial Standards) for materials are generally represented as shown below. There are three parts in JIS standard.

Terminology describing mechanical/physical properties
Different materials have different mechanical and physical properties. Information such as product catalogs usually provides characteristic tables to let users know whether selected materials will satisfy their application needs or create problems.
Use the table below to review the meanings of terms used in characteristic tables.
| Name | Unit of measurement (used in MISUMI catalogs) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength | N/mm2 | The maximum tensile stress per tensile load on the material. |
| Stretch | % | (Material length when pulled and stretched to breaking point – Original length) ÷ Original length |
| Hardness | - | The magnitude of the metal surface's resistance to deformation generated by an external force. JIS standards specify Brinell (HB), Vickers (HV), Rockwell (HR) and Shore (HS) hardness |
| Conductivity (electrical conductivity) | % IACS | An index indicating the ease with which electricity flows in a material. Equal to the reciprocal of electrical resistivity. For industrial applications, the electrical resistivity of a conductor is sometimes expressed by an index that indicates the conductor wire's conductivity as a percentage relative to a value of 100% for annealed copper wire conforming to a standard known as the International Annealed Copper Standard (IACS). |
| Thermal conductivity | cal/(cm・s・℃) | The amount of heat transferred per second in a plate of unit thickness that has a temperature difference of 1°C between each end. |
| Linear expansion coefficient | 10-6/℃ | The rate at which the length of an object increases with each 1°C of temperature rise. |
Mini Column Do you know Ashiyagama tea kettles?
Location of town of Ashiya

Ashiyagama tea kettle (restored)
Ashiyagama is a well known style of Japanese traditional cast iron tea kettle.
The style originated in the town of Ashiya (located in present-day Fukuoka Prefecture). It began in the Kamakura period (1192 to 1333) and had achieved predominance by the Muromachi period (1336 to 1573).
The style is thought to have died out early in the Edo period (1603 to 1867).
Ashiyagama kettles are renowned for their outstanding craftsmanship and aesthetically pleasing shapes and patterns. Eight of the nine tea kettles designated as Important Cultural Properties by the Japanese government are in the Ashiyagama style.
Features of the style include a lightweight construction made possible by a thickness of just 2 mm, rust-resistance and a smooth and glossy surface finish known as namazuhada (literally, catfish skin).
These features were made possible by the use of ironsand, a type of sand with heavy iron concentrations that was abundant in this local area.
Ironsand casting is very difficult and requires a high degree of technical skill.
The level of skill that Ashiyagama craftsmen were able to attain four to eight centuries ago is truly astounding.


