(!)Due to
Microsoft's end of support for Internet Explorer 11 on 15/06/2022, this site does not support the recommended
environment.
Instead, please kindly use other browsers like Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge or Mozilla
Firefox.
- [Temporary Suspension of Order Acceptance for the Middle East] Due to suspension of air transport & courier services to the Middle East region, we regret to inform that we will temporarily stop accepting order(s) until further notice. Thank you for your understanding.
- Notice of End of Sales for Economy Series Pneumatic Equipment Category. More details.
Basic Knowledge of Coupling (Fundamentals of Mechanical Components)
- What is a coupling?
- Coupling variations and features
- How to select a coupling
- Types of coupling and motor
What is a coupling?
A coupling connects a motor to a rotary shaft to transmit power
A coupling (shaft fitting) is a mechanical component used to connect one shaft to another shaft. For example, it is used to connect output shafts of motors to power generators, and to connect the rotary shafts of vehicles to their axles.
Usage example 1: motor + encoder
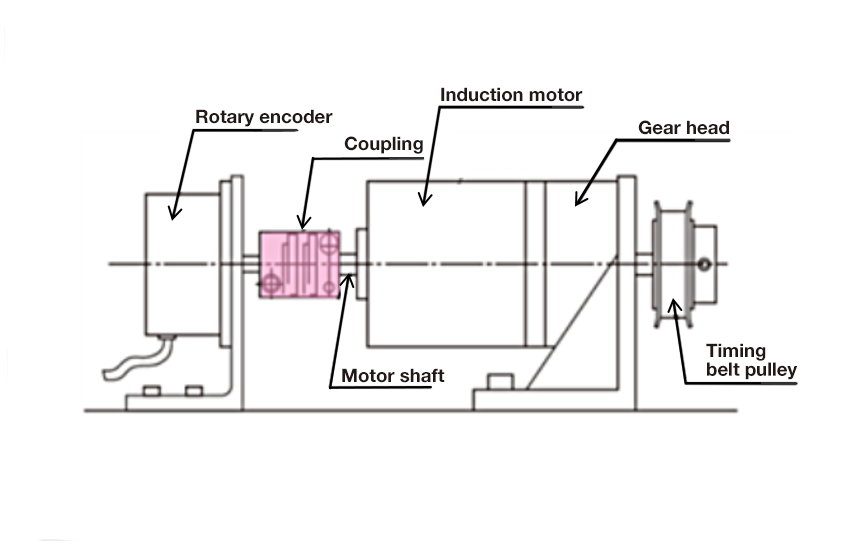
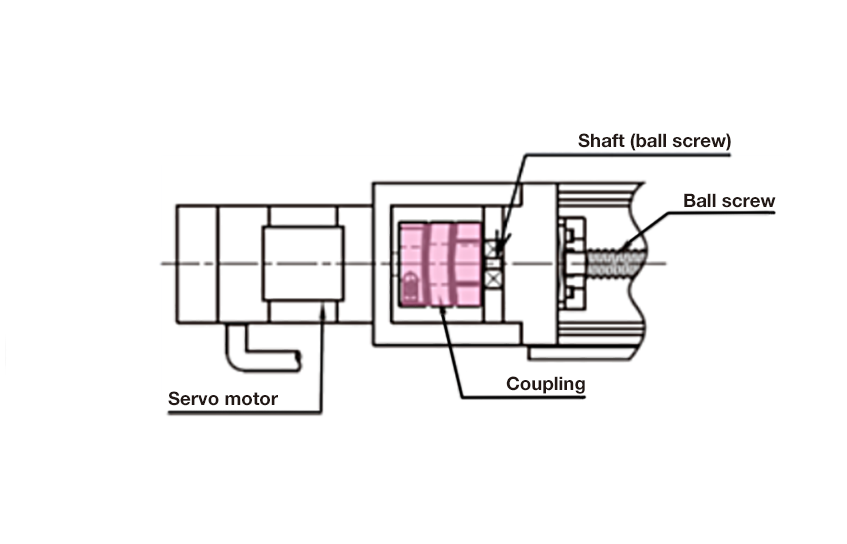
Usage example 2: motor + ball screw
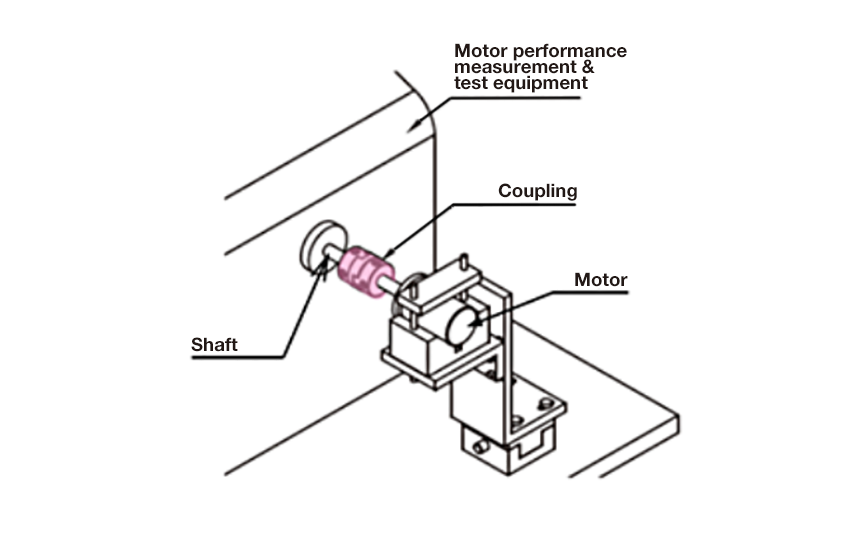
Usage example 3: motor + measurement & test equipment
Role of the coupling
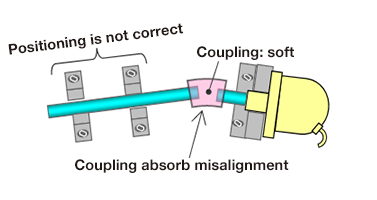
The role of the coupling is to absorb misalignment so that excessive loads are not placed on the motor
When the shafts of different machines are linked, misalignment occurs between the shaft centers. A coupling is able to use the elasticity of components or machine elements to absorb the misalignment while rotating or transmitting power.
When a rigid connection is used

When a coupling is used
Coupling variations and features
The three main variations used in factory automation are disc, slit, and Oldham
Different couplings are used depending on the application. There are a variety of types, including disc, slit, bellows, and rigid types.
Coupling variations
| Type | Disc | Slit | Oldham |
|---|---|---|---|
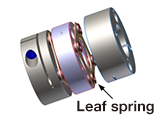
| Structure |
|

|
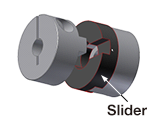
|
| Features |
A leaf spring is inserted between the main bodies, permitting eccentricity,
deviation, and end play. Zero backlash. |
It can be made by milling a solid cylindrical rod. Elasticity is imparted by slit
processing, which permit eccentricity, deviation, and end play. Zero backlash. |
A metal or resin slider is inserted between the main bodies, which permits eccentricity and deviation by sliding. |
| Allowable torque | High | Low | High |
| Allowable misalignment | Low | High | |
| Backlash | No | Yes | |
| Positioning accuracy | High | Low | |
| Motor | Servo motor, stepper motor | Induction motor | |
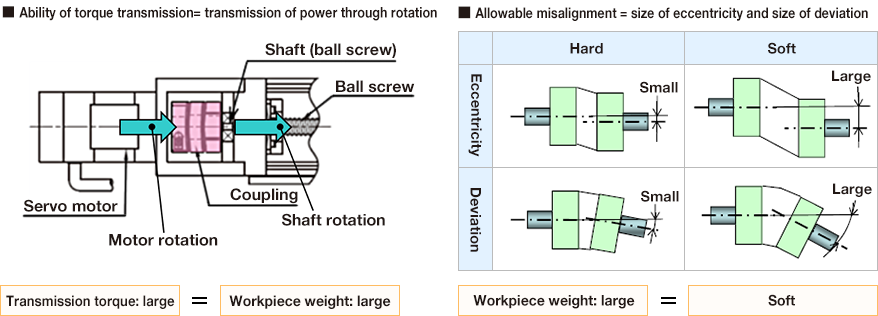
Performance requirements for couplings
Couplings need the ability to transmit torque and to permit misalignment
Connecting shaft to shaft requires accurate (adjustment of) alignment, and endowing the coupling with pliability and flexibility enables it to absorb misalignment.
Figure: Torque transmission ability = transmission of power through rotation, Absorption of misalignment = size of eccentricity and deviation
How to select a coupling
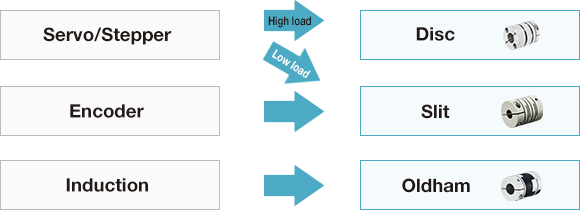
How to select a coupling. The criteria for selecting a coupling vary depending on the type of motor.
STEP 1: Select a variation based on the type of motor
STEP 2 Select outer/inner diameter
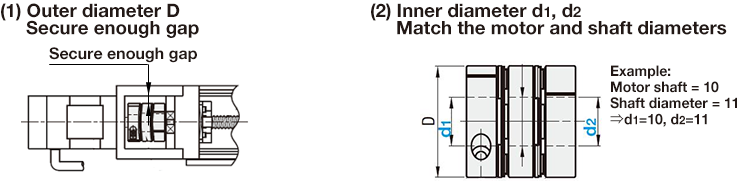
STEP 3 Check the various specifications
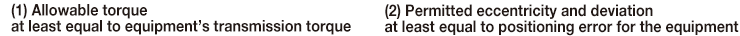
STEP 4 Select a method for installing the shafts
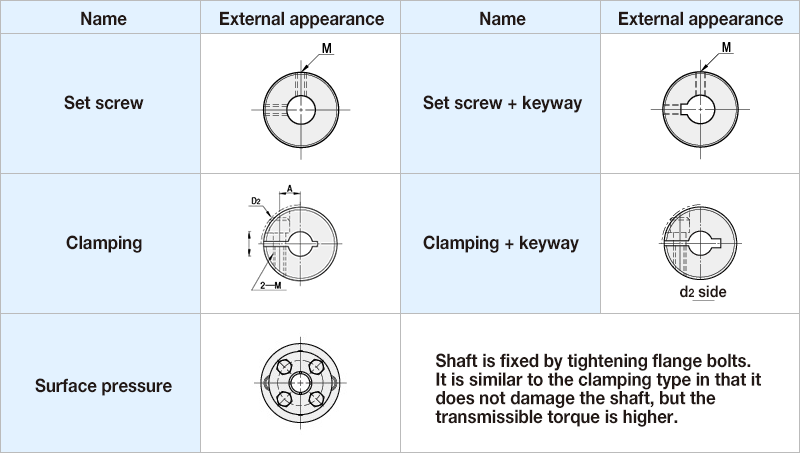
STEP 5 Select double (normal) or single (short)
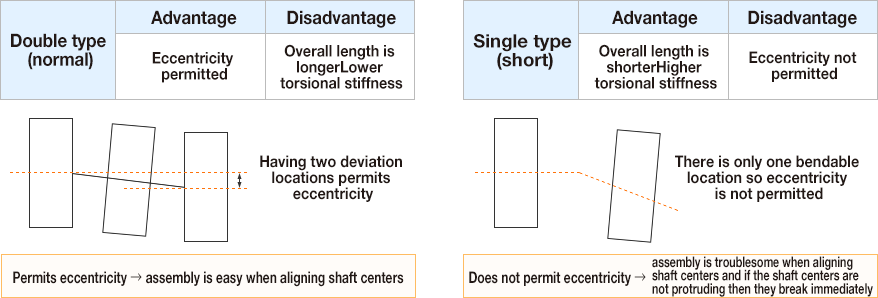
Types of coupling and motor
Examples of motor and coupling combinations. Check the usage conditions, etc. carefully before selecting.
| Type | Servo motor | Stepper motor | Induction motor | Rotary encoder |
|---|---|---|---|---|

|

|

|

|
|
| Features | Equipped with a device to detect speed and positional information, this motor can freely control rotational speed, acceleration, and stopping position. | Operation synchronized with pulsed electricity. Motor that accurately controls positioning using a simple circuit configuration. | It has no control circuit. Ideal for applications involving continuous movement in one direction. | Device to detect motor rotation. There is no load from the encoder itself. |
| Recommended coupling | Disc, slit | Oldham | Slit | |
| Reason for recommendation | Because the control involves rapid acceleration and deceleration as well as forward and reverse rotation, we recommend a zero-backlash, high-stiffness coupling. | In addition to being used for rotation in one direction, it is often used in positions where positioning accuracy is poor, so we recommend a coupling that can deal with high levels of misalignment. | Although rapid acceleration and deceleration as well as forward and reverse rotation are involved, no active load is imposed. We recommend a zero-backlash coupling. | |
| Notable manufacturers |
YASKAWA ELECTRIC CORPORATION Mitsubishi Electric Corporation ORIENTAL MOTOR Co., Ltd. |
MinebeaMitsumi, Inc. Mitsubishi Electric Corporation ORIENTAL MOTOR Co., Ltd. |
Sumitomo Heavy Industries, Ltd. Panasonic Corporation ORIENTAL MOTOR Co., Ltd. |
OMRON Corporation CITIZEN MICRO CO., LTD |




